open
Greater trochanter pain syndrome
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome
Definition
Chronic lateral trochanteric pain
- abductor tendon tendonitis
- trochanteric bursitis
Epidemiology
Women 40 - 60 years old
Mechanism
? repetitive friction of iliotibial tract over GT
Symptoms
Pain over upper lateral thigh with activity
- often related to hip flexion
PVNS
Definition
Pigmented Villo-Nodular Synovitis
- benign inflammatory process that arises in synovial tissues
- contains significant amounts of hemosiderin
Epidemiology
Age: 20 - 50
Sex: M > F
Types
A. Diffuse
- throughout joint synovium
- more difficult to treat / excise fully
Open Acromioplasty
Described by Neer / modified by Rockwood
Two Step Acromioplasty
1. Anterior acromioplasty
- resect anterior acromion back to ACJ
- prevent impingement in flexion
2. Resect anteroinferior acromion
Technique
Position
- beach chair
- mark anatomy
- limb draped free
Open Bankart Repair
Aim
Repair of the anterior capsule & avulsed labrum to anterior glenoid
- anatomic repair
Usually combined with a capsular shift
Contraindications
Bony bankart > 25% glenoid
Technique
Position
- beach chair position
- arm free
- Mayfield head ring / Spyder and Tmax
Biceps Tenodesis
Options
Arthroscopic
- intra-articular
- suprapectoral
Open
- suprapectoral
- subpectoral
A. Arthroscopic Intra-articular
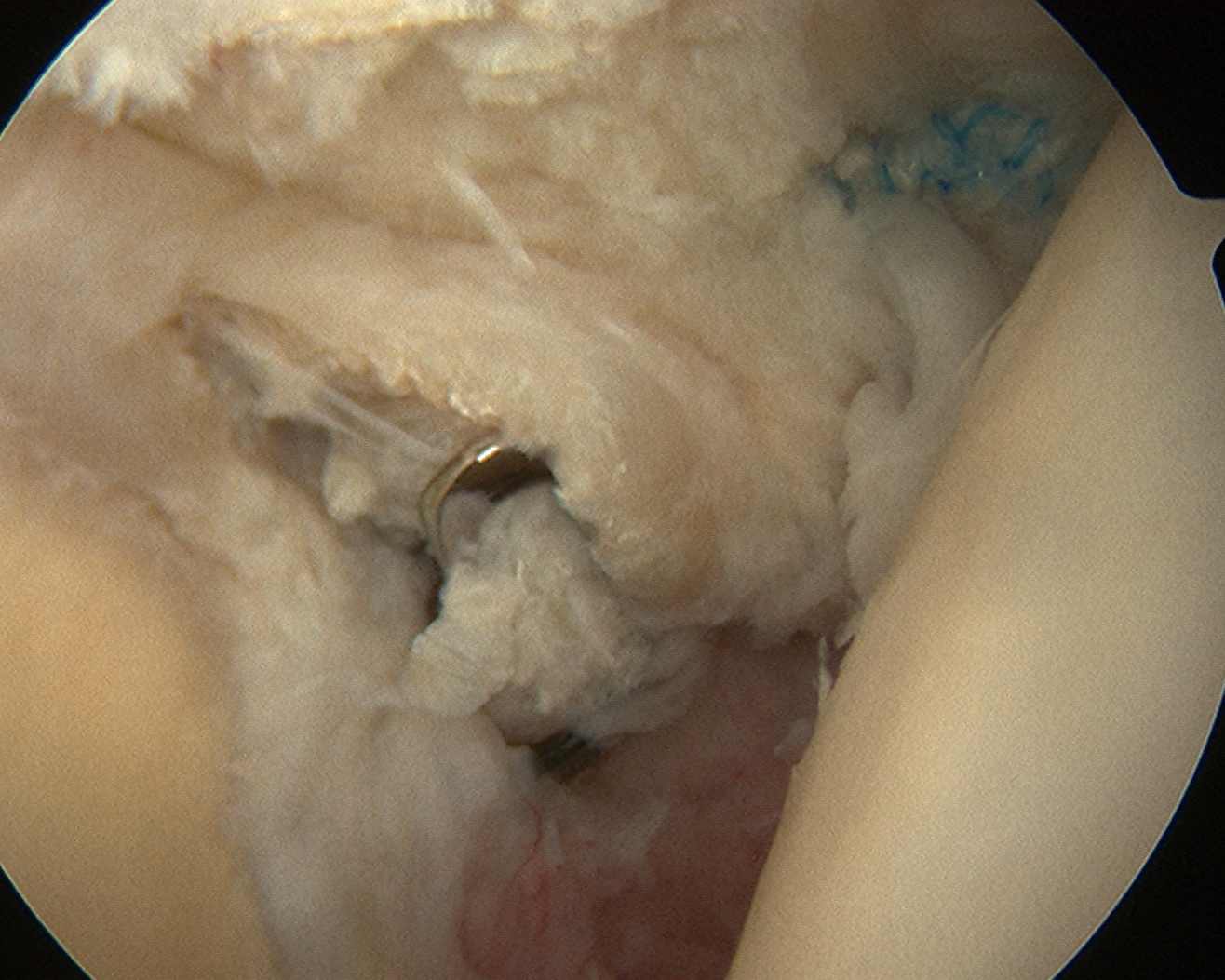
Concept
Subtalar and Triple Arthodesis
Biomechanics
Able to achieve relatively high level of function after STJ fusion
- previously believed that isolated STJ fusion should not be performed
- believed that triple arthrodesis was operation of choice for hindfoot
- STJ fusion has superior result with less stress on AJ
Average loss of DF 30% / PF 10%
Position of hindfoot determines flexibility of transverse tarsal (CCJ & TNJ) joints
- imperative that fusion be positioned in ~ 5o valgus
Arthrodesis
Indications
Indications have narrowed
- due to success of shoulder arthroplasty
1. Chronic infections of GHJ
2. Stabilization in paralytic disorders
3. Post-traumatic brachial plexus palsy
4. Salvage of failed GHJ Arthroplasty
- may need bone graft procedures
5. Arthritic diseases unsuitable for arthroplasty / young patient
ACJ Osteoarthritis
Aetiology
Post-traumatic (type III clavicle fractures)
Idiopathic
4 patterns
1. OA with osteophytes
- contribute to impingement
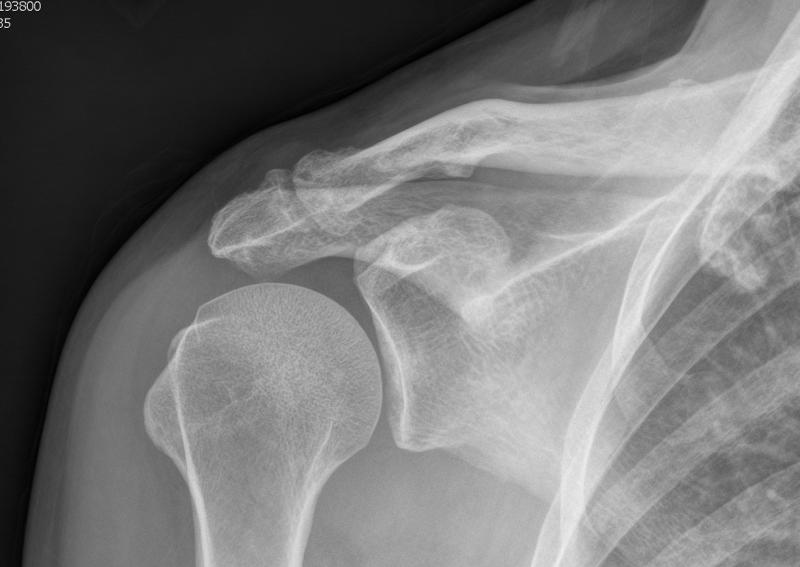
2. Osteolysis with resorption & gross osteoporosis
Lateral Epicondylitis / Tennis Elbow
Incidence
Lateral : Medial 9:1
Epidemiology
4th & 5th decades
- M = F
- 75% dominant arm
50% of regular tennis players
- especially > 2 hrs / week
Aetiology
Insertion pathology / Enthesopathy
Over-extension of the elbow with supination / pronation
Anatomy
Lateral epicondyle
- anconeus from posterior face
- ECRB and EDC from anterior face (CEO)
