Anatomy
Saddle shaped bone
- located between talus and 3 cuneiforms
- critical to medial longitudinal arch
Blood supply
- enters medially and laterally
- central third relatively avascular
Types
1. Dorsal lip avulsion fractures
- most common
- talonavicular ligament avulsions
- non operative treatment
2. Tuberosity fractures
- can be avulsion tibialis posterior
- can be accessory navicular
3. Body fractures
- traumatic
- stress fractures
Navicular Stress Fractures
Epidemiology
Young athletes
Repetitive stress
Chronic pain with no distinct injury
Xray
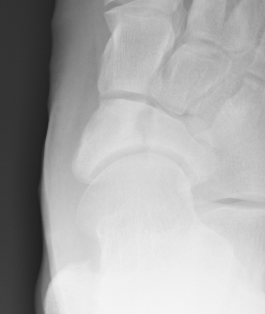
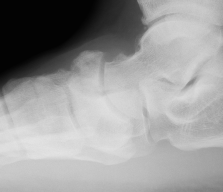
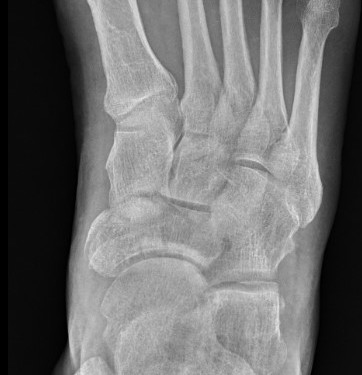
Displaced navicular stress fracture
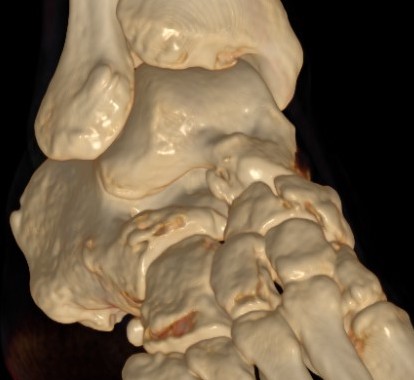
CT
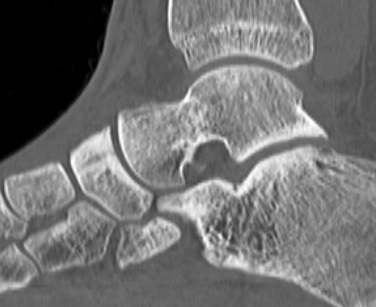
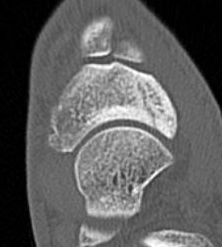
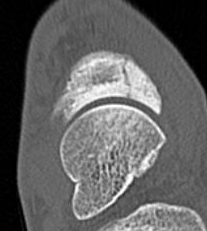
Minimally displaced navicular stress fracture
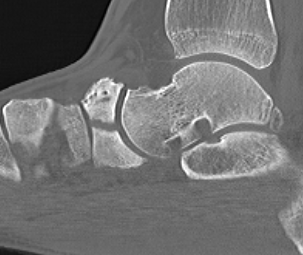
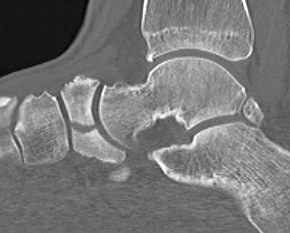
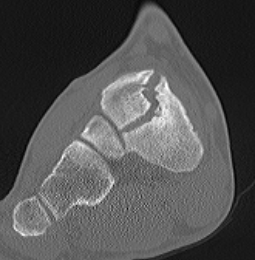
Displaced navicular stress fracture
MRI
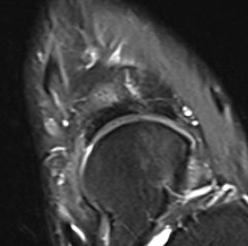
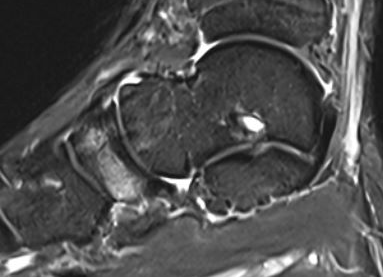
Minimally displaced navicular stress fracture
Stress fracture classification
Type I: Dorsal cortical break - nonoperative
Type II: Fracture extends to mid body
Type III: Fracture breaches two cortices - operative
Nonoperative Management
Indication
Undisplaced
Failure nonoperative treatment
Method
Strict non-weight bearing
Bone stimulator
Careful observation - can displace




Results
- systematic review navicular stress fractures
- nonoperative management: 78% success with 24% refracture
- operative management: 98% success with 1% refracture
- 110 patients with navicular stress fracture
- most common sports track and field, gymnastics
- mean age 15, 65% female
- nonoperative in cast / boot successful in 85%
- longer return to sport with surgery
Saxena et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2017
- 62 navicular stress fractures
- CT most accurate modality
- 11% refracture rate with non operative care
- 13% developed osteoarthritis
- overall return to sport 92%
Operative management
Indications
Nonunion
Displacement
Approach
Dorsomedial approach
- between EHL and Tibialis anterior
AO foundation dorsomedial approach
Screw technique
AO foundation navicular screw technique
Consider debridement / drilling / bone graft for displaced, sclerotic stress fractures
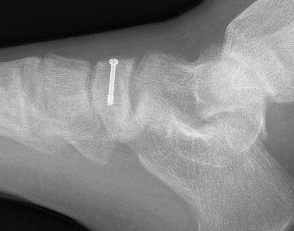
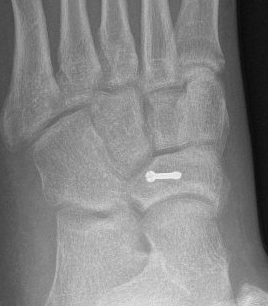
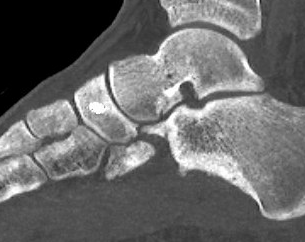
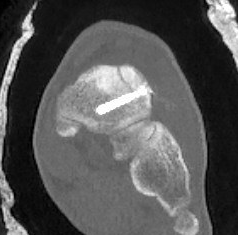
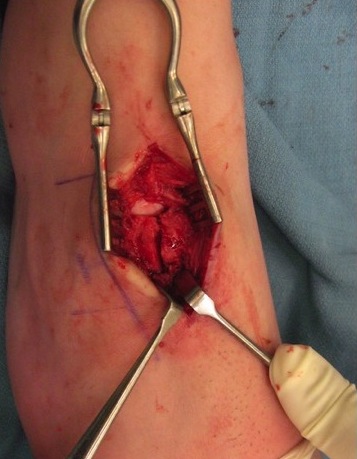


Displaced stress fracture treated with single screw
Locking plate
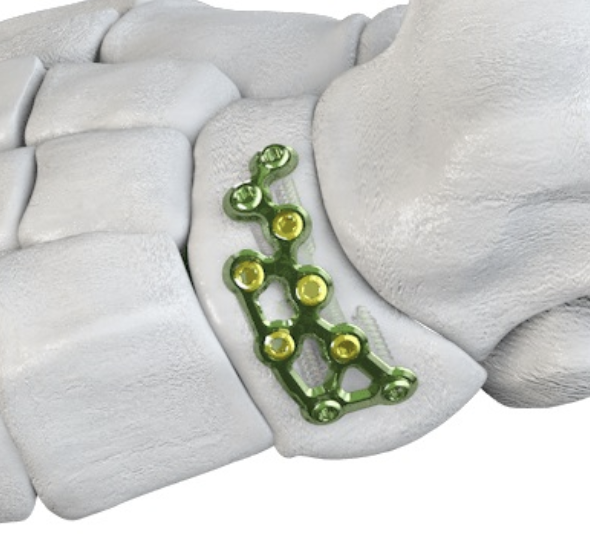
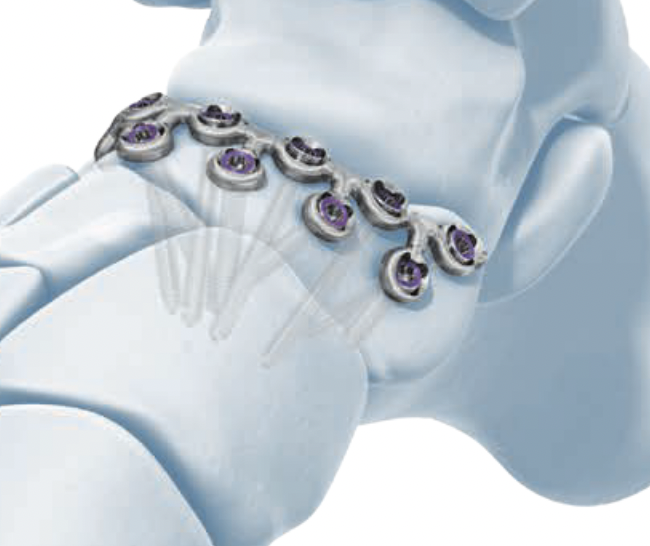
Paragon navicular plate Synthes navicular plate
AO foundation navicular locking plate technique
Paragon Baby Gorilla navicular plates PDF


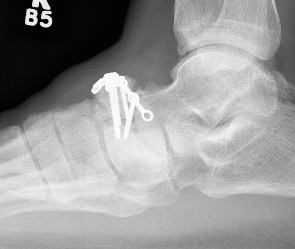
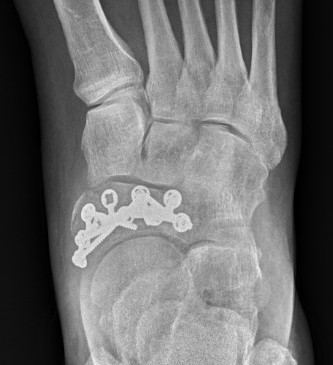
Displaced stress fracture treated with dorsal plate
Results
- 10 navicular stress fractures treated surgically
- 80% united on CT scan
- nonunion associated with complete / displaced fractures preoperatively
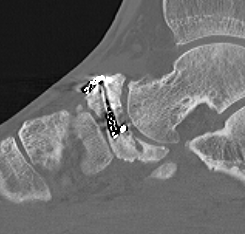
Acute Navicular Body Fractures
Mechanism
High energy injuries
Imaging


Acute, minimally displaced navicular fracture


Acute displaced navicular fracture

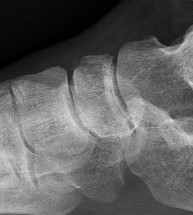
Acute displaced navicular fracture
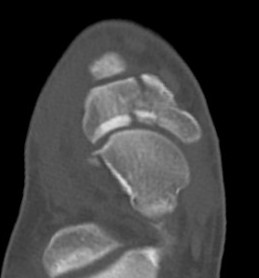
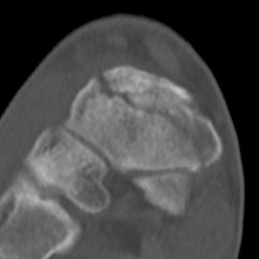
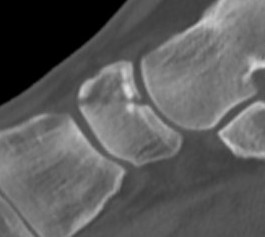
Acute displaced navicular fracture
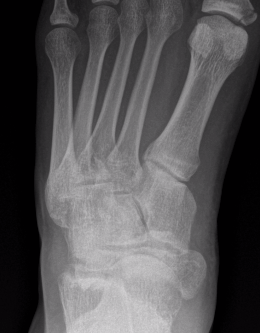
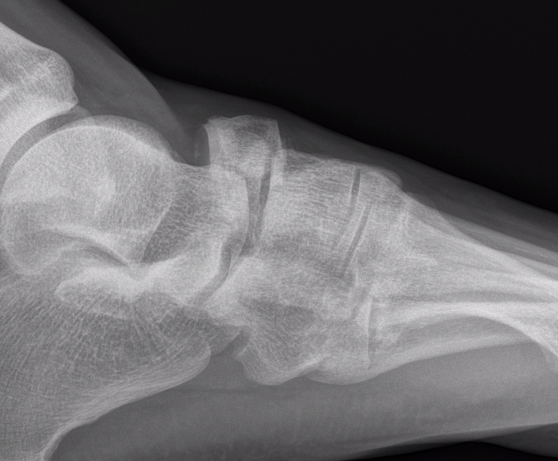
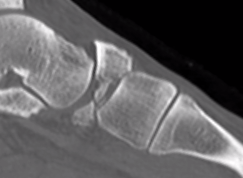
Acute displaced navicular fracture
Operative management
Indications
Displacement
Goal
Imperative to maintain medial column length
Options
Screw
Dorsal locking plate
Bridging medial plate - talus to 1st metatarsal
Temporary external fixation
Primary fusion

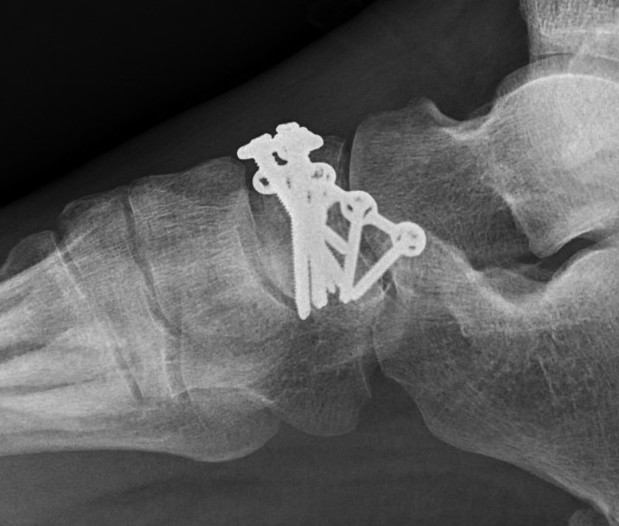
Acute traumatic fracture treated with navicular plate

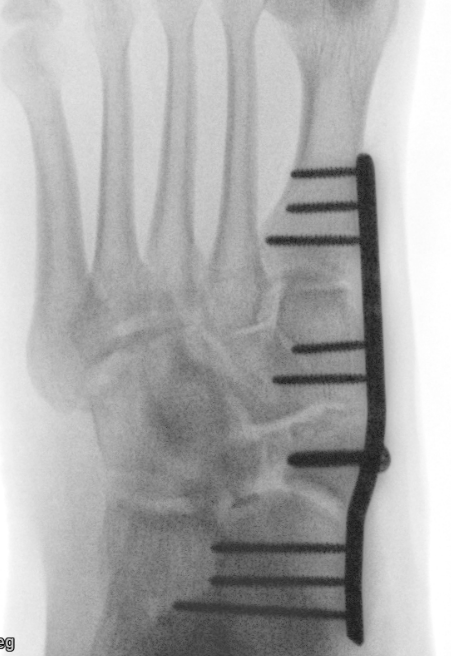
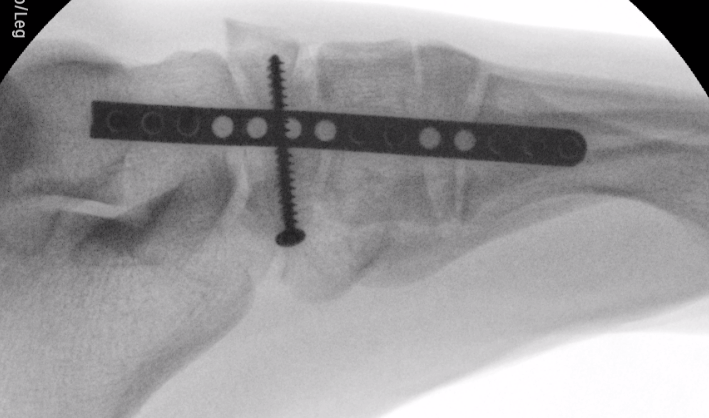
AO foundation medial bridge plate technique
